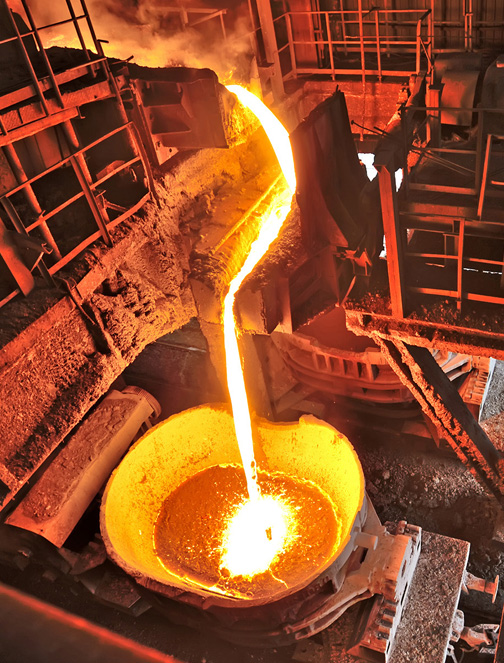
This Carbon Steel JIS S45C Plates can be used below oxidizing situations as much as 1300 Degree C (2370 Degree F), a lot better than traditional nickel-chromium alloys.The alumina layer is likewise a barrier to carburization and suffixation. Carbon diffusion rates into the bottom steel are substantially reduced, as is the adherence of carbon deposits at the oxide surface. The exceptionally clean surface below carburizing situations additionally continues first-rate heat transfer rates in radiant heating and chemical processing applications, as a result lowering the chance of harm to the alloy via overheating.
Cutting with abrasive calls for its care to keep away from thermal oxidation that can purpose for cracking; but if it is feasible then cooling fluid must be used in the process. The adherent aluminium oxide scale formed via way of means of the alloy gives a surface barrier to sulphur. The entire absence of nickel within this Carbon Steel DIN 1.1191 Plates avoids the formation of dangerous nickel sulphide. Its hardness is within the variety and the work hardening rate is exceptionally low as compared with nickel-base alloys. The well-known machining traits are just like ferrite steel. Although it is feasible to apply excessive-speed steel equipment it is also greater low-priced to appoint carbide-tipped equipment.